Temporary Works
References: R Record keeping requirement | E An engineering/certification requirement | P A permit to work requirement | S A safe work method statement (SWMS) / written plan
Note: This section is to be read in conjunction with the Temporary Works Matrix and the following sections:
- General
- Risk Management - safety in design risk workshops
- Gantries and Hoardings
- Training and Competency Schedule
- Permit to Work
- Civil and Demolition (all)
- Structure (all)
- Plant and Equipment (all)
- Cranes Hoists & Lifting (all)
- Work@ Heights (all)
Explanatory Note: Temporary Works Matrix
The Temporary Works Matrix (Guide Design and Construct Projects) has been developed by Multiplex as a framework to promote questioning, assessment and reasoning for the level of review and controls that may be implemented to eliminate or, if this is not reasonably practicable, minimise the risks to health and safety (i.e. risk of failure) in consideration of the variables that may be associated with temporary works activities. Temporary works can be categorised and defined in terms of the level of complexity, refer to Table 1.
Table 1: Temporary works categories and levels of complexity (design) and definition.

Note: Similar references to risk categories are described in Temporary Works Risk Guidelines (Australia).
Importance levels that inform design requirements (based on risk) are discussed in AS3610 Formwork for concrete, AS1170 - Minimum design loads on structures, AS 4100 – Steel Structures and the National Construction Code
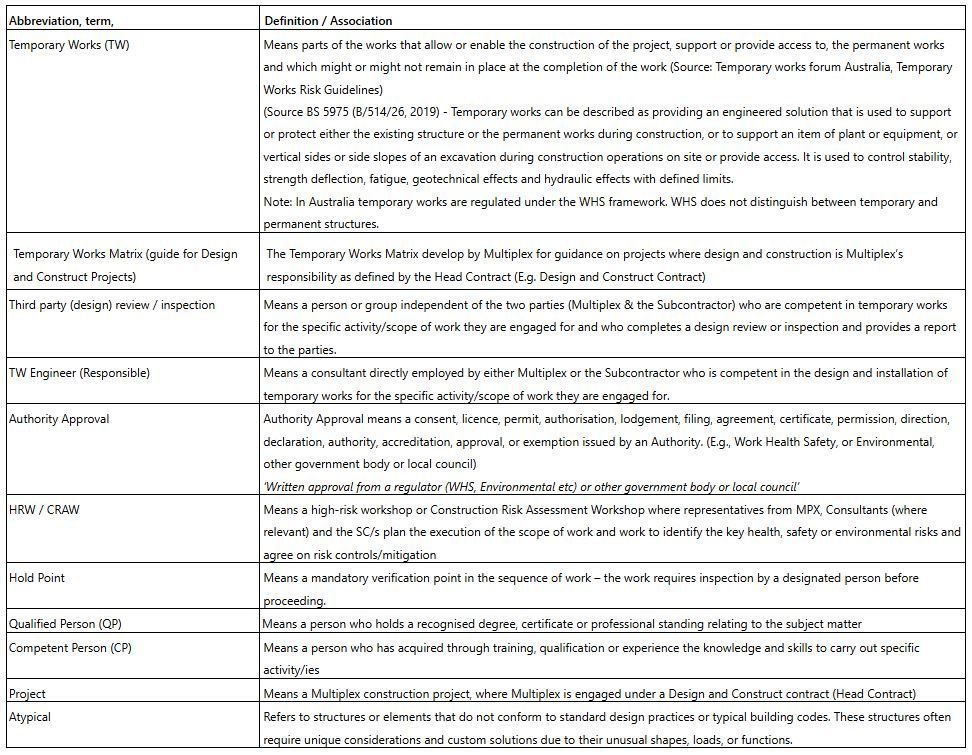
Definitions
Table 2: Definitions
Design and Planning
R Project contract and tender reviews should incorporate an evaluation of TW and the level of complexity of TW that applies to the Project.
R TW activities must be included as applicable in Tender / Agreement (Consultancy / Subcontract) scopes of works , Project / design risk workshops, high-risk workshops / construction risk assessment workshops or similar.
R As applicable Subcontract, Consultancy or similar Agreements must clearly identify TW obligations, capability, competence, responsibilities etc. and include the Multiplex Temporary Works Matrix (Guide for Design and Construct Projects).
R The Project management team should progressively during the construction stages (e.g. Demolition, Excavation, Structure etc) complete a review of TW applicable to the Project and allocate/record responsibilities as depicted on the Project-specific Temporary Works Register (TW-R) or similar.
R In completing the review of Project TW activities, identify the TW activities and sub-activities apply to the Project and evaluate the TW activities / sub activities and the applicable category / level of complexity
Note: Where a Project incorporates the imposition of temporary or permanent loads, or excavation within the zone of influence of an existing structure or part of an existing structure, then
- Structural and geotechnical investigation must be carried out to the extent necessary to form an assessment of the existing structure's capacity, to verify that it meets the requirements of the planned TW loads or if modification or support is required.
- Investigations should include physical inspection, review of any documentation, and where applicable testing.
Table 2: Temporary works categories, definition and management actions

E Documents depending on the TW category/level of complexity are required to be developed by the applicable consultant/subcontractor, and include
- Design brief/statement
- Concept design (drawings)
- Detailed design drawings (incl. sequence)
- Calculations
- Technical specifications
- Work Method Statement/s
E The documents/drawings or SWMS prepared must describe the stages of work where specified in the Multiplex Temporary Works Matrix and identify critical elements or stages and any Hold Points required (e.g. when the temporary structure or element can be loaded or unloaded, continued, struck, propping removed etc.). Note: Work sequences may apply to both temporary works and /or the sequence of permanent works construction (or demolition).
TW planning and sequencing should consider consequences for situations where the TW is left in place for an unscheduled/prolonged period, contingencies should be in place to verify the ongoing integrity of the TW.
Operational
MPX must coordinate the Projects TW between the applicable parties. TW activities must be performed as designed and described in the TW documents and drawings.
S Subcontractor SWMS should incorporate applicable TW activities and controls. Workers carrying out TW activities must be inducted into the applicable SWMS, have access to the applicable TW documents / drawings and hold valid records of competency / training (as applicable), evidence must be retained on site.
TW activities must be supervised by competent persons in accordance with the Multiplex Temporary Works Matrix and Training and Competency Schedule as specified by the responsible TW Engineer.
R Subcontractors (where applicable) should prepare and implement TW activity specific Inspection and Test Plans/Checklists that include Hold Points / inspections required for the installation, monitoring (where required), and dismantling of the TWs in accordance with the responsible engineer’s specifications.
R Inspections to verify the TWs stability / structural integrity must be carried out by competent / qualified persons in accordance with the Multiplex Temporary Works Matrix and/or as specified by the responsible TW Engineer.
Where extreme weather is forecast or experienced, TW should be reviewed, assessed and stabilised prior to the expected weather event and inspected post weather event (I.e. prior to the re-commencement of related works). Where it is identified that the TW has been affected / compromised, the responsible TW Engineer must be consulted, remediation action determined and carried out, prior to the re-commencement of related works.
R Alterations that may affect the integrity of the TW elements are not permitted unless authorised by the responsible TW Engineer and reviewed by MPX. Authorisation to modify TW must be in writing from the responsible TW Engineer and be received by MPX before proceeding with any alterations.
Where it is identified that the temporary works is not performing as design intended or its being impacted by other work (e.g. impact was unforeseen / not planned), the TW activity must be suspended / made safe, and an assessment carried out by the responsible TW Engineer. If any changes to the TW are required, the responsible TW Engineer must review/approve any changes. In cases where the responsible TW Engineer is unavailable another TW Engineer of equivalent (or higher) qualification may approve the change.
References
Temporary Works Matrix (Guide for Design and Construct Projects)
Temporary Works Risk Guidelines 2020: Temporary Works forum Australia
Temporary Works Procedural Control - Good practice guideline: Temporary Works forum Australia
WHS Legislation (All states/territories, Commonwealth)
Code of Practice (Safe Work Australia) – Safe Design of Structures
Code of Practice (WA) - Safe Design of Structures
Documents
WA - WA HSE P-TW REG 308
Document Control
Version 1 December 2024 – New Standard







